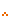Options
Definition
Options contracts give buyers the right (not obligation) to buy / sell the underlying assets at a specific time and strike price. If the option is exercised, seller must have an obligation to fulfill the transaction. In short, options are classified into call options and put options.
Types of Options
To make it simple, option premium consists of intrinsic value and time value. Out-of-the-money options consists merely time value and only in-the-money options contains intrinsic value. Intrinsic value is the price difference between the exercise price and the asset price at a specific point of time.
Premium = Intrinsic Value + Time Value
Option Pricing Model
Binomial and Black-Scholes are two most popular models calculating option premium. The Binomial model mainly assumes the price of the underlying asset will move up and down based on certain probabilities, with the prevailing stock price as latest option theoretical value. The original Black-Scholes model is used to calculate the pricing of European options (no dividends). By keying in information including the exercise price, underlying asset price, risk-free interest rate, days to maturity and volatility, the theoretical value of the option can be calculated. Common Strategy - Single Strategy
Portfolio Strategy
Options contracts give buyers the right (not obligation) to buy / sell the underlying assets at a specific time and strike price. If the option is exercised, seller must have an obligation to fulfill the transaction. In short, options are classified into call options and put options.
Types of Options
- Call Options
Gives the buyer the right (not obligation) to buy the underlying assets at / before the specified time (depends whether it is a European or American option) at a strike price as specified in the contract. If the buyer chooses to enforce the right to exercise the option, the other party (seller) must have the obligation to sell the assets or pay the difference in cash value between the settlement price and the strike price. - Put Options
Gives the buyer the right (not obligation) to sell the underlying assets at /before the specified time (depends whether it is a European or American option) at a strike price as specified in the contract. If the buyer chooses to enforce the right to exercise the option, the other party (seller) must have the obligation to buy the assets or pay the difference in cash value between the settlement price and the strike price. - Special Options
Standardized options are usually traded on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange, and special options with non-standardized terms are traded in the OTC market in recent years.
To make it simple, option premium consists of intrinsic value and time value. Out-of-the-money options consists merely time value and only in-the-money options contains intrinsic value. Intrinsic value is the price difference between the exercise price and the asset price at a specific point of time.
Premium = Intrinsic Value + Time Value
Option Pricing Model
Binomial and Black-Scholes are two most popular models calculating option premium. The Binomial model mainly assumes the price of the underlying asset will move up and down based on certain probabilities, with the prevailing stock price as latest option theoretical value. The original Black-Scholes model is used to calculate the pricing of European options (no dividends). By keying in information including the exercise price, underlying asset price, risk-free interest rate, days to maturity and volatility, the theoretical value of the option can be calculated. Common Strategy - Single Strategy
| 1. | Long Call Options Buy Call Option with Exercise Price S |
||||||||
 |
|||||||||
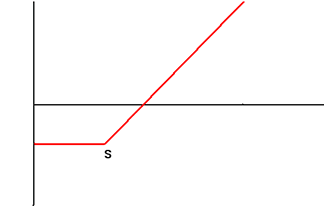
| 2 | Short Call Options Sell Call Option with Exercise Price S |
||||||||
 |
|||||||||
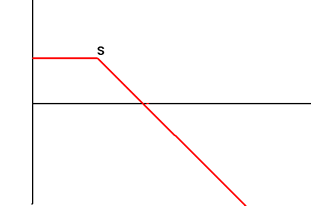
| 3 | Long Put Options Buy Put Option with Exercise Price S |
||||||||
 |
|||||||||
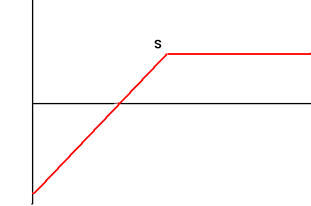
| 4. | Short Put Options Sell Put Option with Exercise Price S |
||||||||
 |
|||||||||
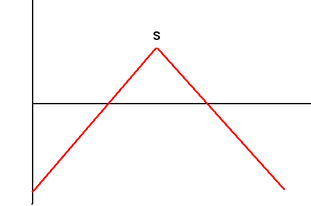
| 1. | Long Straddle Buy Call and Put Options with Exercise Price S and Same Maturity |
||||||||||||||||
 |
|||||||||||||||||
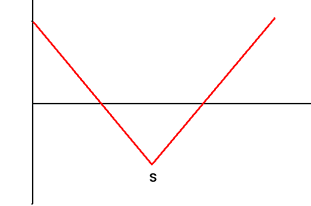
| 2 | Short Straddle Sell Call and Put Options with Exercise Price S and Same Maturity |
||||||||||||||||
 |
|||||||||||||||||
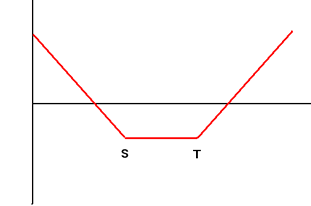
| 3 | Long Strangle Buy Put Option with Exercise Price S and Call Option with Exercise Price T with the same maturity at the same time |
||||||||||||||||
 |
|||||||||||||||||
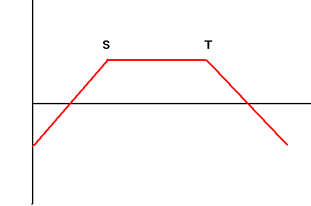
| 4. | Short Strangle Sell Put Option with Exercise Price S and Call Option with Exercise Price T with the same maturity simultaneously |
||||||||||||||||
 |
|||||||||||||||||
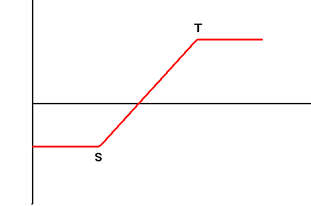
| 5. | Bullish Call Spread Buy Call Option with Exercise Price S and Sell Call Option with Exercise Price T with the same maturity simultaneously |
||||||||||||||||
 |
|||||||||||||||||
| 6. | Bullish Put Spread Buy Put Option with Exercise Price S and Sell Put Option with Exercise Price T with the same maturity simultaneously |
||||||||||||||||
 |
|||||||||||||||||
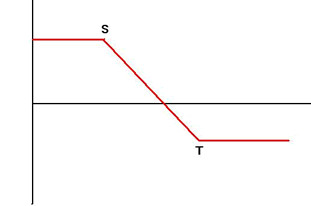
| 7. | Bearish Call Spread Sell Call Option with Exercise Price S and Buy Call Option with Exercise Price T with the same maturity simultaneously |
||||||||||||||||
 |
|||||||||||||||||
| 8. | Bearish Put Spread Sell Put Option with Exercise Price S and Buy Put Option with Exercise Price T with the same maturity simultaneously |
||||||||||||||||
 |
|||||||||||||||||
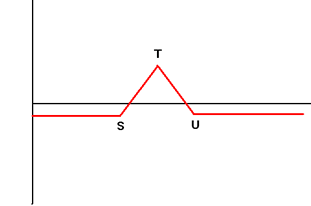
| 9. | Long Butterfly Buy Call (Put) Option with Exercise Price S, Sell 2 Call (Put) Options with Exercise Price T, Buy Call (Put) Option with Exercise Price U Condition: T - S = U - T |
||||||||||||||||
 |
|||||||||||||||||
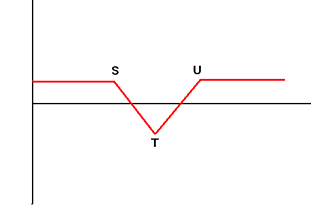
| 10. | Short Butterfly Sell Call (Put) Option with Exercise Price S, Buy 2 Call (Put) Options with Exercise Price T, Sell Call (Put) Option with Exercise Price U Condition: T - S = U - T |
||||||||||||||||
 |
|||||||||||||||||